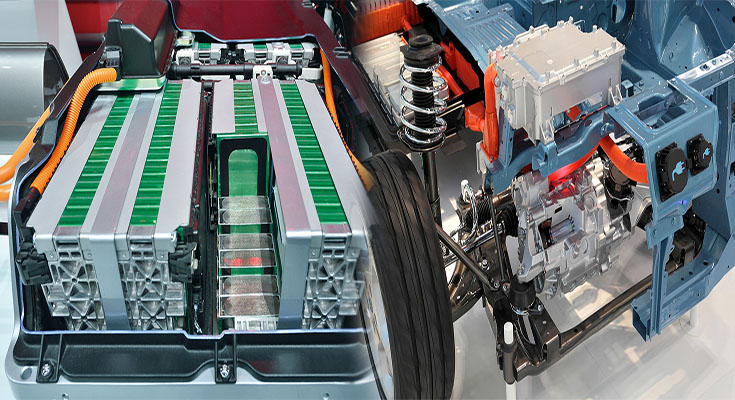
A battery electric vehicle is a car that runs solely on electricity. These vehicles can travel farther on a single charge than conventional gas-powered cars, but their overall effect on the environment depends on where they’re driven.
The batteries in these cars store chemical energy and convert it to electricity. Typically, these are lithium-ion batteries.
What is a BEV?
A battery electric vehicle (BEV) is a car that uses electricity to power its motor and drive the wheels. BEVs don’t produce tailpipe pollution because the electricity they use comes from the grid or renewable sources like wind and solar.
The electric motor in a BEV runs on the electricity stored in the battery pack, which is a big pack of batteries containing hundreds of individual cells. These are scaled up versions of the lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries found in mobile phones and laptops.
These Li-ion batteries are rated in kilowatt-hours, which tell you how much energy they can hold before running out. An EV with a larger kWh rating can go further than one with a smaller kWh.
How does a BEV work?
Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) are cars that are powered solely by a large, lithium- ion battery. This big pack consists of thousands of tiny lithium-ion cells working together, each one capable of storing hundreds of watts of power.
These EV batteries are vastly different to the heavy lead-acid batteries in most conventional combustion engine cars and offer a massive increase in lifespan. They also work on a far more efficient and reliable alternating current than traditional power grids, which allows for faster charge times.
The energy in a BEV battery is pumped to an electric motor, which spins the wheels and gives the car its power. The EV motor has 90% fewer moving parts than an internal combustion engine (ICE) and produces less emissions.
Charging a BEV is easy – just plug the vehicle into a wall box or public charging point and you’re good to go. Many chargers can charge up to 80% in 30 minutes.
What are the benefits of owning a BEV?
There are several benefits to owning a battery electric vehicle (BEV). They are clean, simple and cost-effective to run.
One benefit is that there are no oil changes or other fluids like engine oil, which saves on maintenance expenses. Another benefit is that EVs generally last much longer than conventional gas-powered vehicles.
EVs have a higher energy efficiency than gasoline-powered cars, meaning they use less fuel to travel the same distance. And that savings adds up to a substantial amount of money.
Besides the financial benefits, owning an EV is a great way to help reduce your environmental impact. Moreover, if you are concerned about range anxiety, a BEV lets you swap out the hassle of recharging your car for the convenience of Level 2 or DC fast chargers at home, on public streets and pretty much anywhere there is an outlet.
What are the drawbacks of owning a BEV?
A battery electric vehicle (BEV) is an alternative to a traditional gas-powered car. They are more energy efficient; they produce no tailpipe emissions and require little maintenance.
However, they have a few drawbacks, which are worth considering before you decide to purchase one. First, they typically have a higher initial cost than a gas- powered vehicle.
Second, they may need a home charging station. Luckily, there are many public stations across the country, but many people prefer to have one in their home.
Third, BEVs often have shorter ranges than a gas-powered vehicle. This can be a big concern for some drivers, especially if they enjoy long road trips.
Additionally, the batteries of modern EVs are expected to last for about a decade and replacing them can be expensive. Fortunately, there are federal and state incentives available to help offset these costs. Also, their cost is expected to go down as technology advances.